Macros in Excel are a game changer for productivity. They allow you to automate complex tasks with just a click. They eliminate hours of manual work from processing large datasets to generating reports instantly. However this power comes with a serious warning. Yet, malicious macros can act as a Trojan horse, delivering malware, stealing data or even taking your system control. However, cybercriminals often exploit macros by embedding harmful code in seemingly innocent documents. It makes security a top significance.
The good news? You don't have to avoid macros altogether. You can safely connect their efficiency while keeping your PC secure with the right precautions. This guide will cover how to enable macros in Excel without compromising your system. So, you can confidently automate it.
What Are Macros in Excel?
Macros in Excel are powerful scripts designed to automate repetitive tasks and transform multi step processes into a single tick. You can record them once as a macro and let Excel handle the rest instead of manually performing the same actions frequently. Yet, this functionality is handy for tasks like data cleaning, report generation or applying complex formatting guidelines.
1. How Macros Work: Recording and Playback
At their core, macros operate by recording your actions—keystrokes, menu selections, and formula entries—and saving them as instructions. Excel repeats those exact steps automatically while running the macro later. As if you frequently format sales data in a specific way, it can replicate that formatting instantly to save your valuable time.
2. Common Uses of Macros in Business and Data Analysis
Macros are widely used in financial modeling, automating revenue projections, or expense tracking calculations. They're also indispensable for generating recurring reports, updating dashboards, or processing large datasets. Macros can streamline administrative tasks, such as sorting email lists or preparing standardized documents.
3. The Role of VBA in Macros
Just behind every macro is VBA or Visual Basic for Applications. It is Excel's built-in programming language. However the macro recorder provides a simple way to create basic automation. VBA allows for more sophisticated customization like conditional logic or interacting with other software. You don't need to learn VBA to use macros effectively because the recorder suffices for most routine errands.
Why Macros Can Be Dangerous
However, macros may be designed to save time. They can become a serious security threat in the wrong influences. Yet, the same automation that makes them useful for legitimate tasks allows them to execute harmful actions without your information. So, understanding the risks is crucial before enabling macros in any Excel document.
1. The Threat of Macro Viruses
Macro virus is a malicious code embedded within an Excel file disguised as harmless macros. It can replicate itself, corrupt data, or even spread to other files on your system when enabled. These viruses exploit Excel's automation features unlike traditional viruses that require software vulnerabilities. It makes them surprisingly easy to deal out. For example, a seemingly innocent invoice attachment could contain a macro that once enabled silently installs malware.
2. How Malicious Macros Infect Your System
Yet, malicious macros typically work by tricking users into enabling them. Often, attackers disguise infected files as essential documents. For example financial reports, order confirmations or even internal company letters. Excel may display a security warning when you open the File. But, the hidden code executes if you override it and enable macros. It could lead to data theft, ransom ware attacks or unauthorized access to your system. However, some macros manipulate Excel's settings to weaken future security warnings and leave your PC vulnerable to further outbreaks.
3. The Golden Rule: Only Enable Macros from Trusted Sources
Since macros run with the same permissions as the user. They can modify files, access sensitive data or connect to external servers anything. The safest approach is to enable macros only when you are certain of the File's source. Yet, trusted sources include verified colleagues, official company documents or well-known platforms. It does not include unsolicited email attachments or unfamiliar websites.
How to Enable or Disable Macros in Excel for Windows
1. Open Excel on your Windows computer.
2. Click File in the top-left corner.
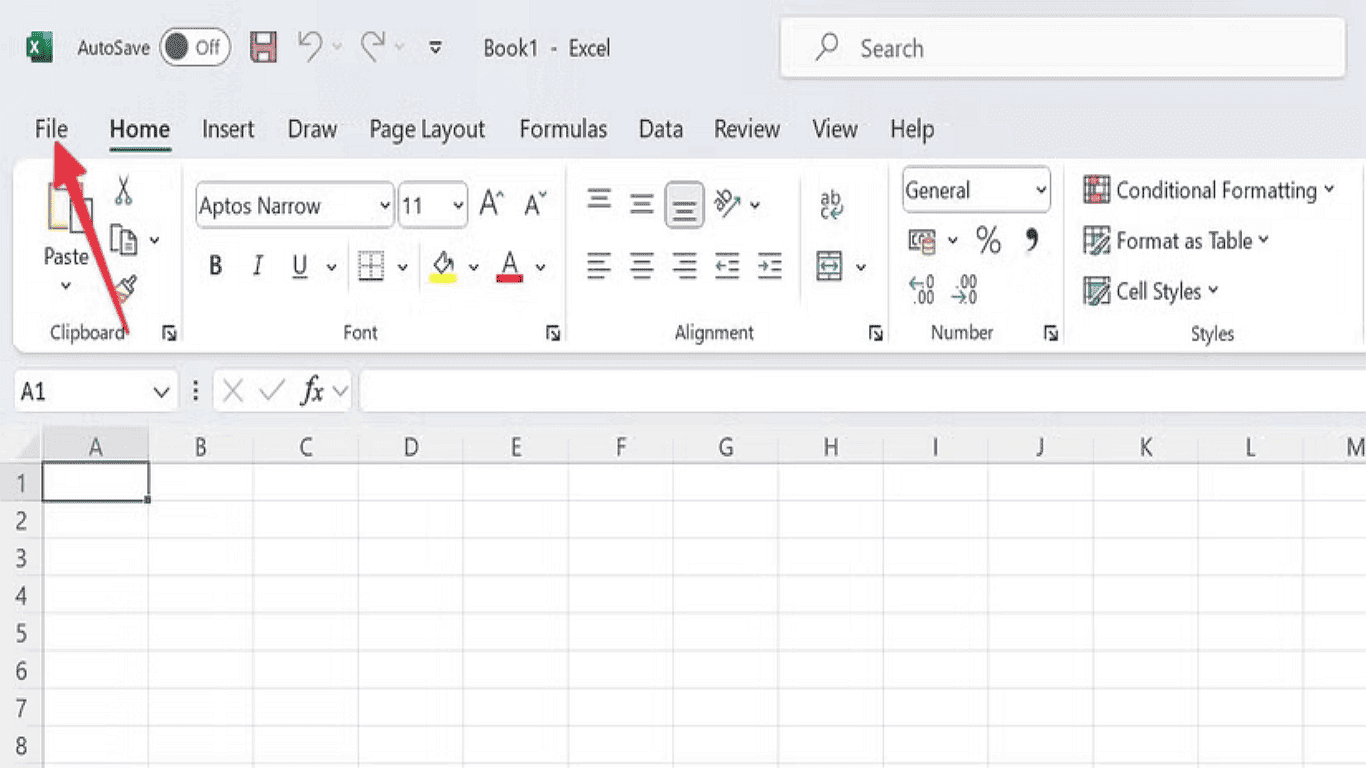
3. Choose More, then select Options.
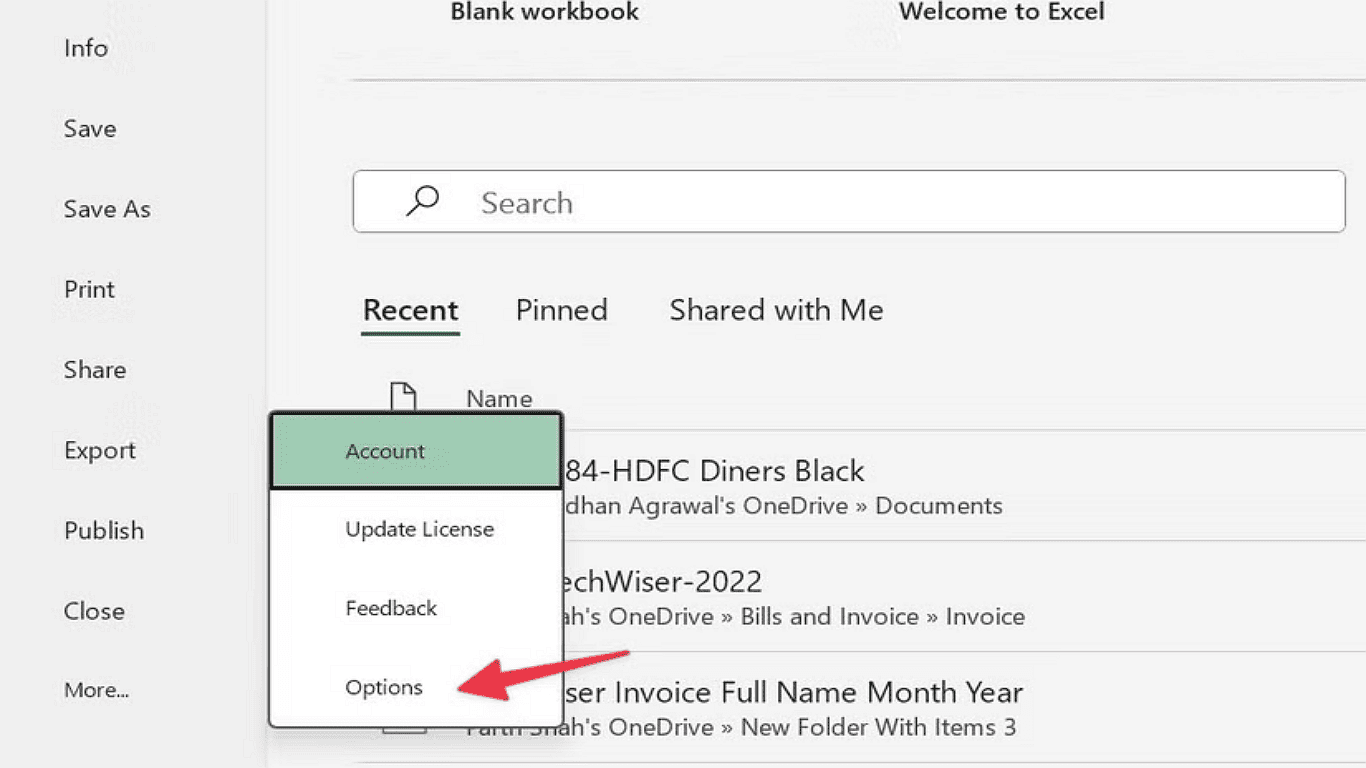
4. In the Excel Options window, click Trust Center, then open Trust Center Settings.
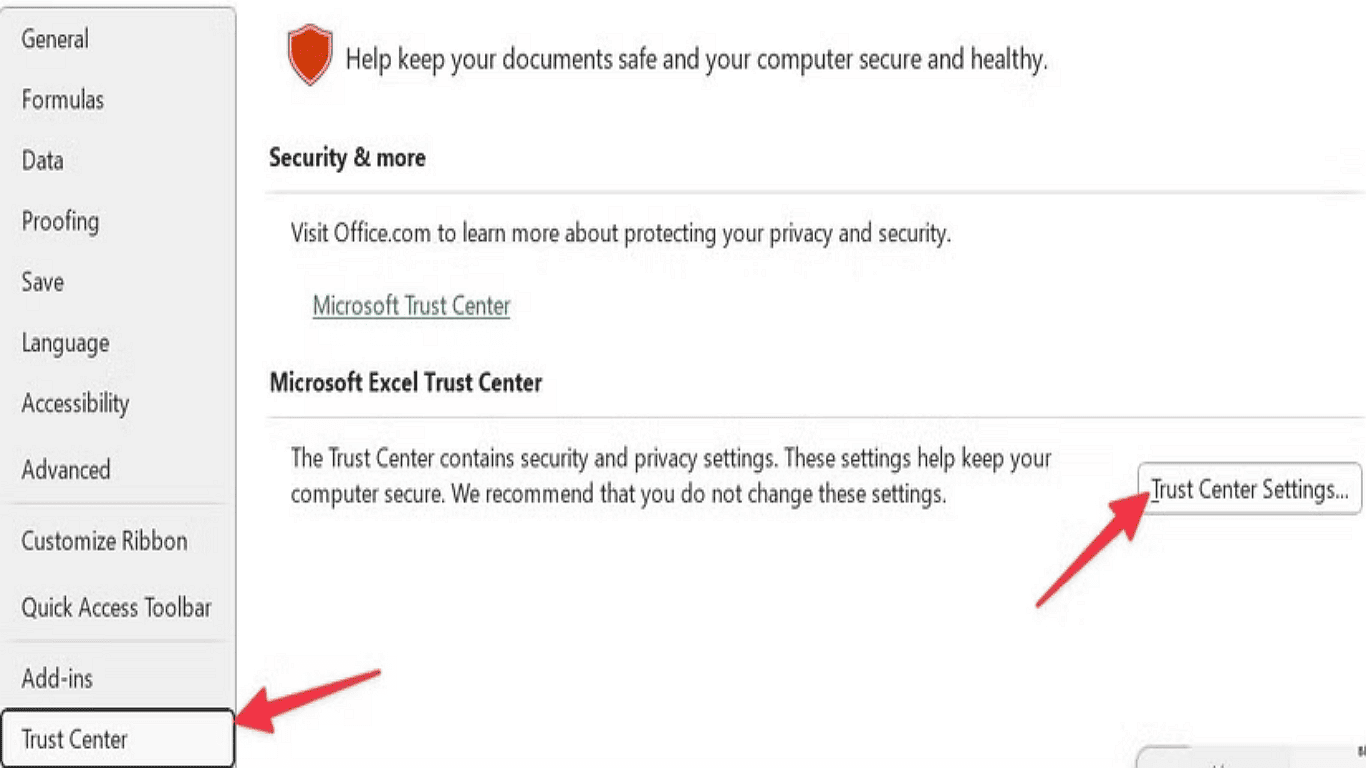
5. Click on Macro Settings to view and modify your preferred options.

Here, you'll find four options.
Understand the Security Options
Excel provides four levels of macro security:
1. Disable all macros without notification (Most restrictive)
Completely blocks all macros without any alerts. Choose this if you never use macros or work in high-risk environments.
2. Disable all macros with notification (Recommended setting)
Shows the standard security warning bar when opening files with macros. This balanced approach lets you selectively enable trusted content while maintaining security.
3. Disable all macros except digitally signed ones.
Only allows macros from publishers who have verified digital signatures. You'll need to pre-approve these signatures under Trusted Publishers.
4. Enable all macros (Not recommended)
Turns off all security warnings, automatically running every macro. Avoid this setting as it leaves you vulnerable to malicious code.
Additional Considerations
- System administrators often enforce specific macro policies through Group Policy for business environments.
- If you choose the digital signature option, you must establish a certificate authority or obtain certificates from trusted providers.
- These settings apply to all future Excel sessions until changed again.
How to Enable Macros in a Specific Excel File
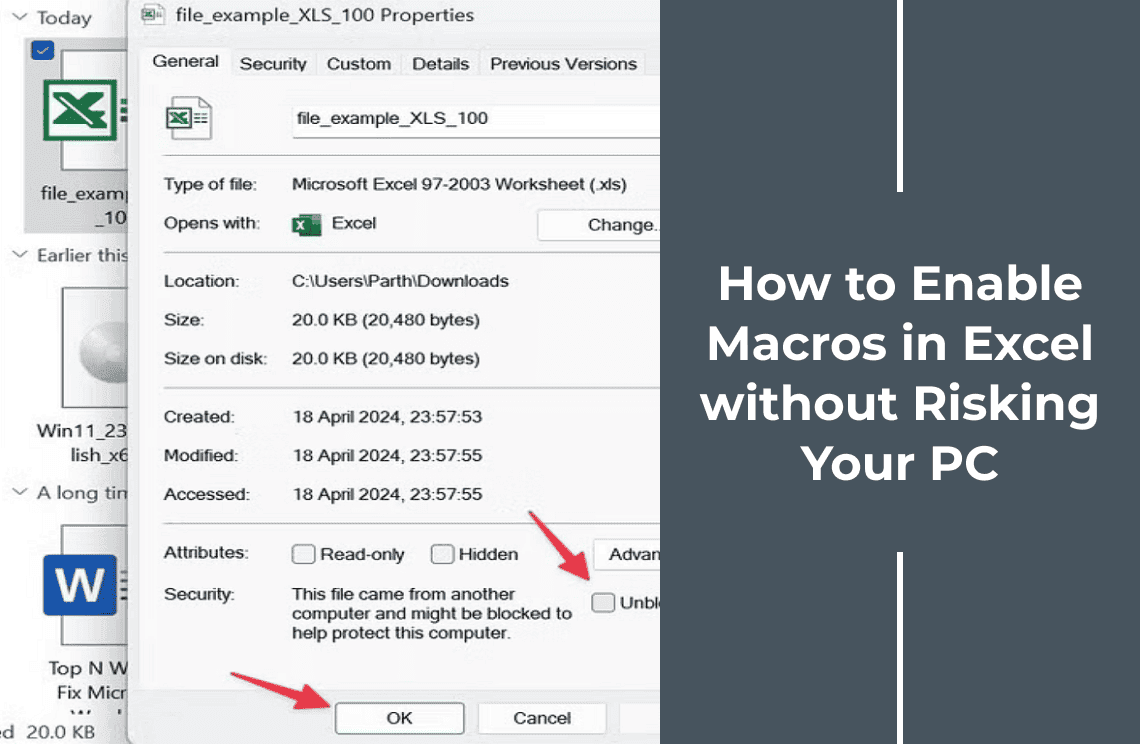
Microsoft may disable macros by default and display a security alert when opening an Excel file from an untrusted source. However, you can adjust the file's properties to bypass this warning and enable macros.
1. Open File Explorer and navigate to the folder containing the Excel file.
2. Right-click the file and choose Properties from the menu.
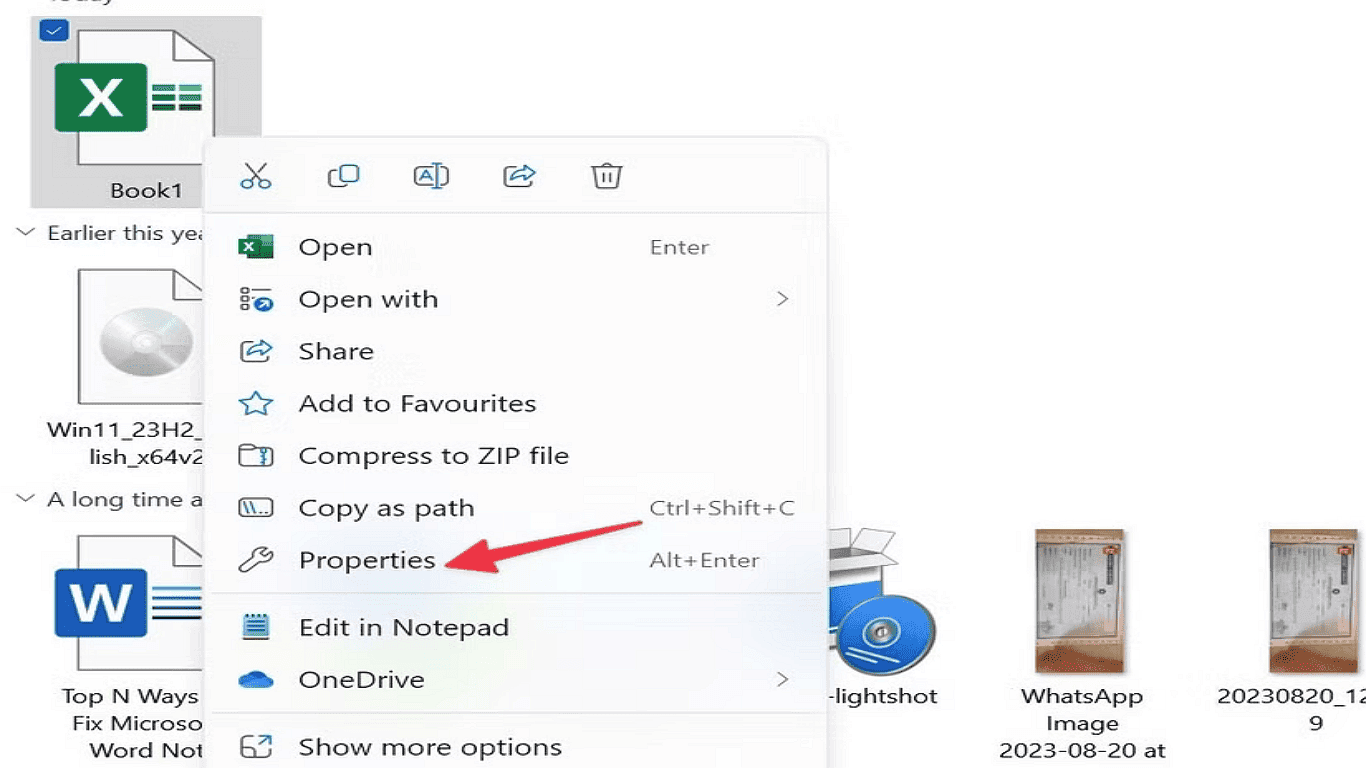
3. In the Properties window, locate the Security section.
4. Check the Unlock option, then click Apply and OK to confirm.
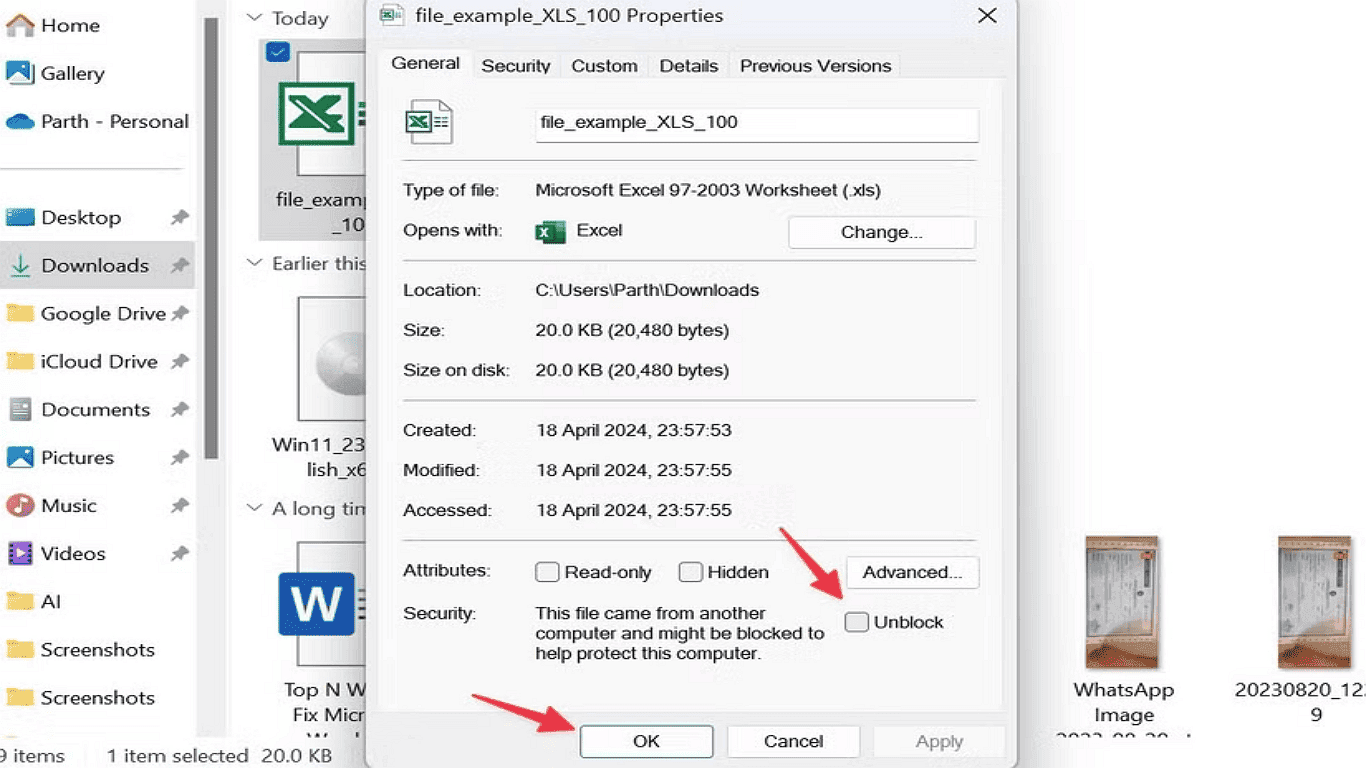
It will allow macros to run without the security prompt for this specific file.
Set Up a Trusted Location for Macros in Excel
Trusted locations allow Excel to open files without security warnings, automatically enabling macros. Files stored in these folders are considered safe, so the Trust Center skips macro checks.
Important
Only Designate Secure Folders As Trusted Locations To Avoid Potential Risks.Steps to Add a Trusted Location:
1.Open Excel Options (follow the previous steps if needed).
2.Go to Trust Center > Trust Center Settings.
3.Select Trusted Locations from the left menu.
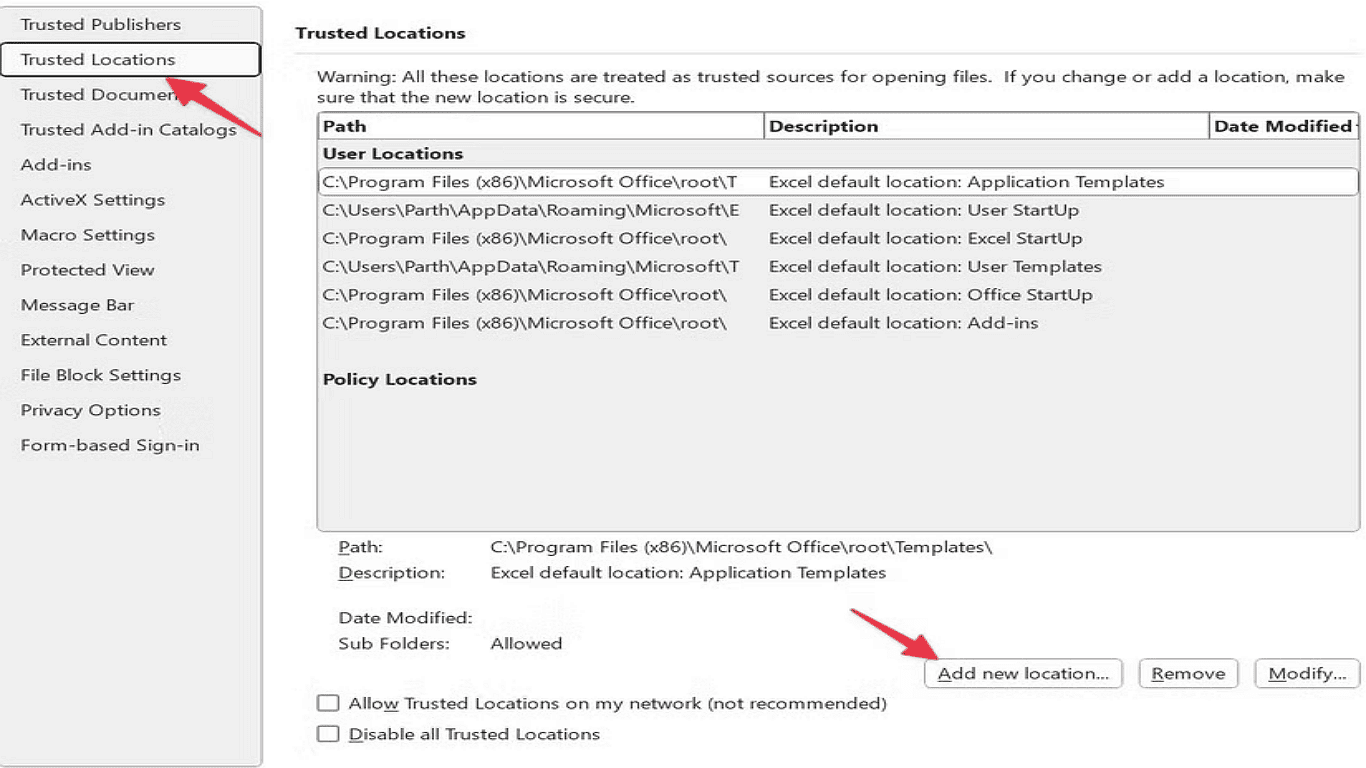
4.Click Add New Location to include a folder.
You can also:
- Remove an existing trusted location.
- Allow network locations (not recommended).
- Disable all trusted locations.
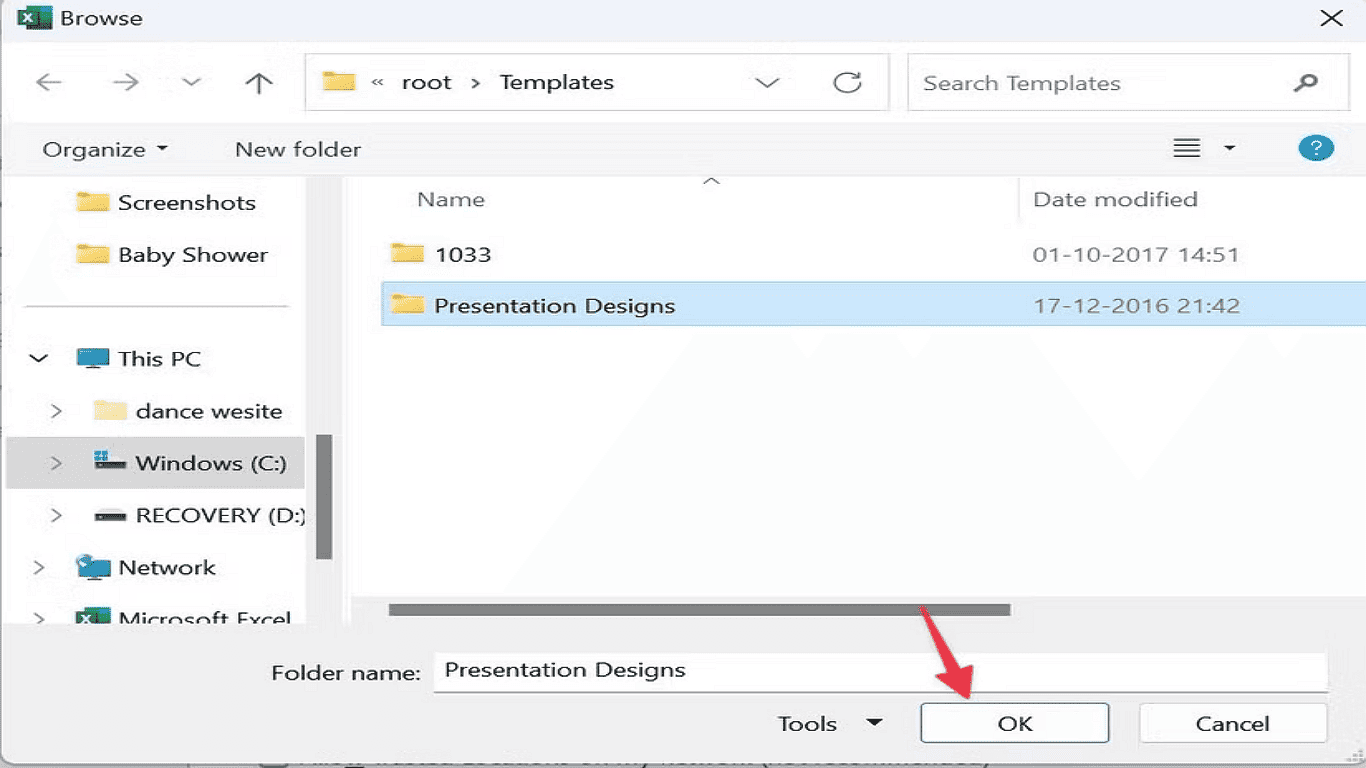
5.Click Browse and navigate to the desired folder.
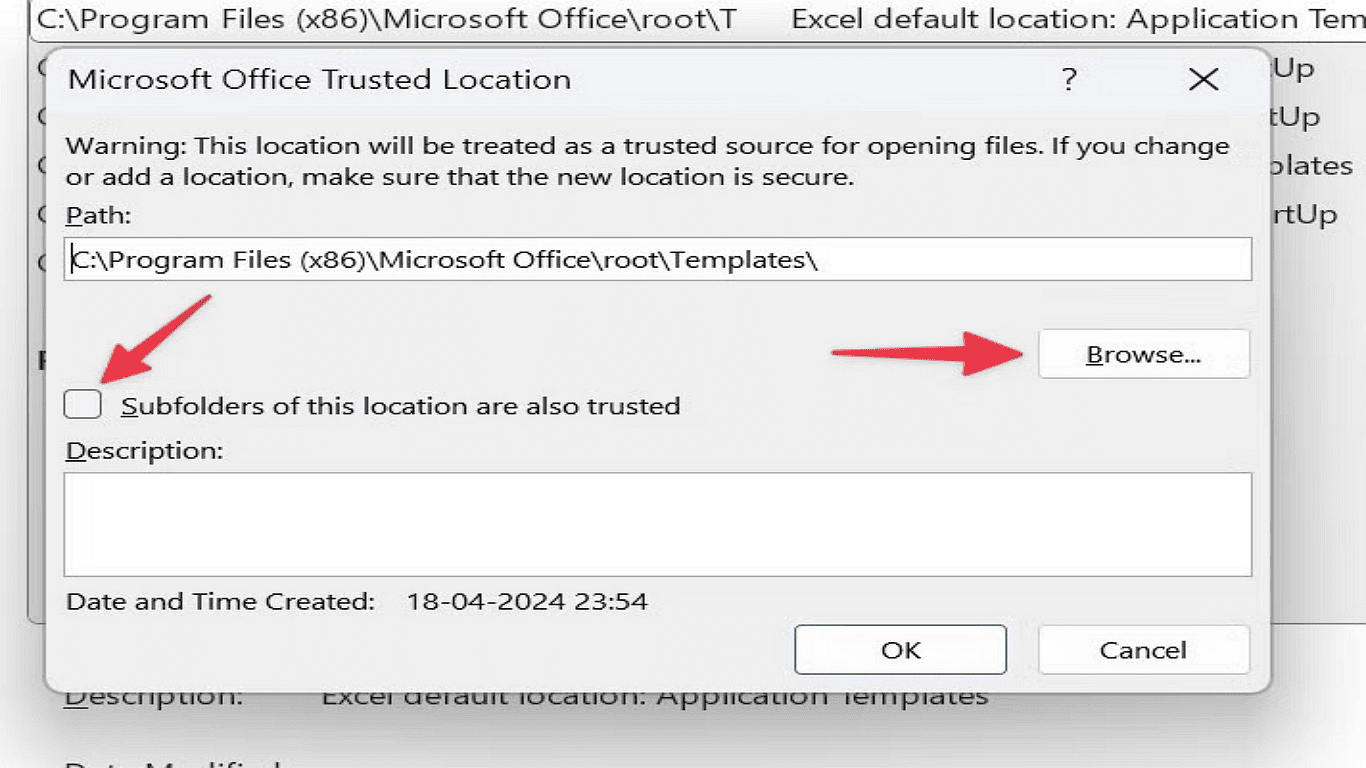
6.Select OK to save your changes. Excel will now trust all files stored in this location, enabling macros to run automatically without security prompts.
How to Enable and Disable Macro Settings in Excel for Mac
Mac users can adjust macro security preferences in Excel with these steps:
1.Launch Microsoft Excel on your Mac
2.Click the Excel menu in the top menu bar
3.Select Preferences from the dropdown
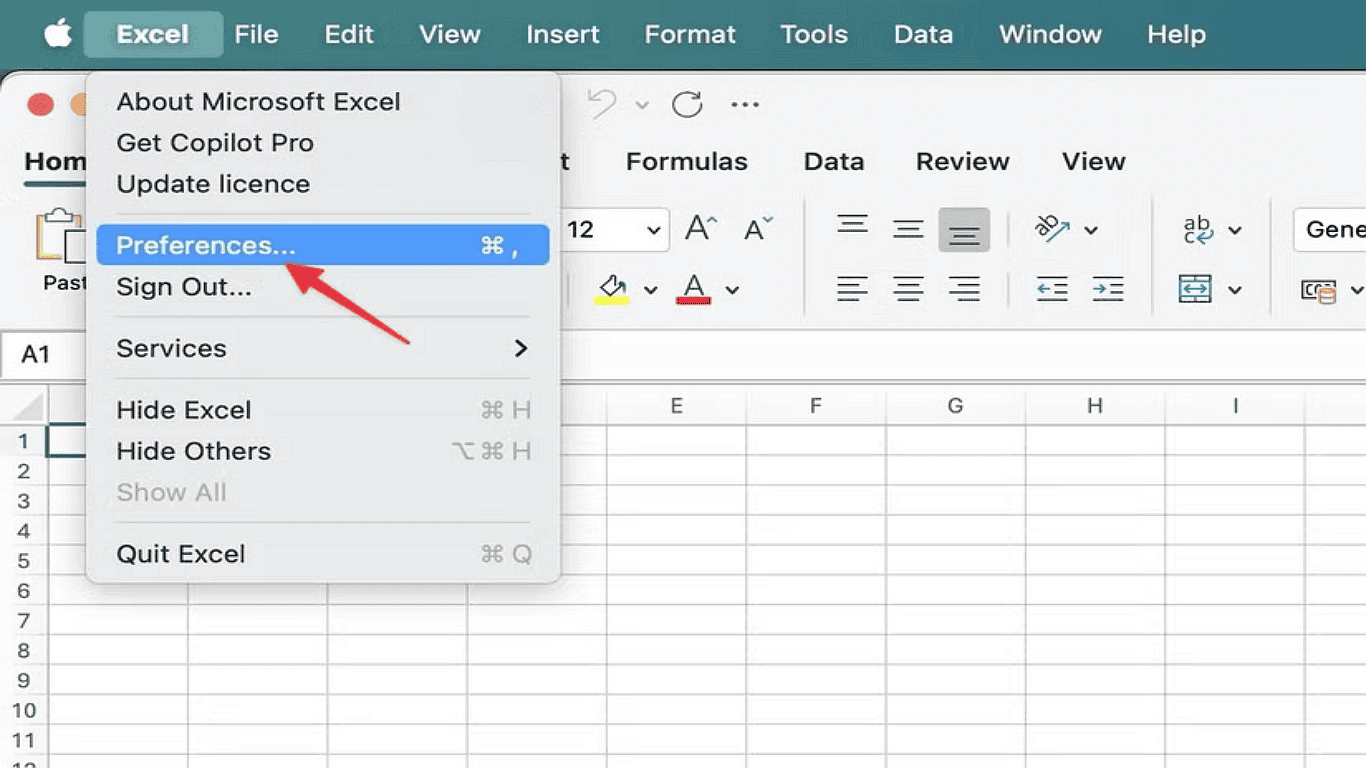
4.In the Preferences window, choose Security (located under Sharing and Privacy)
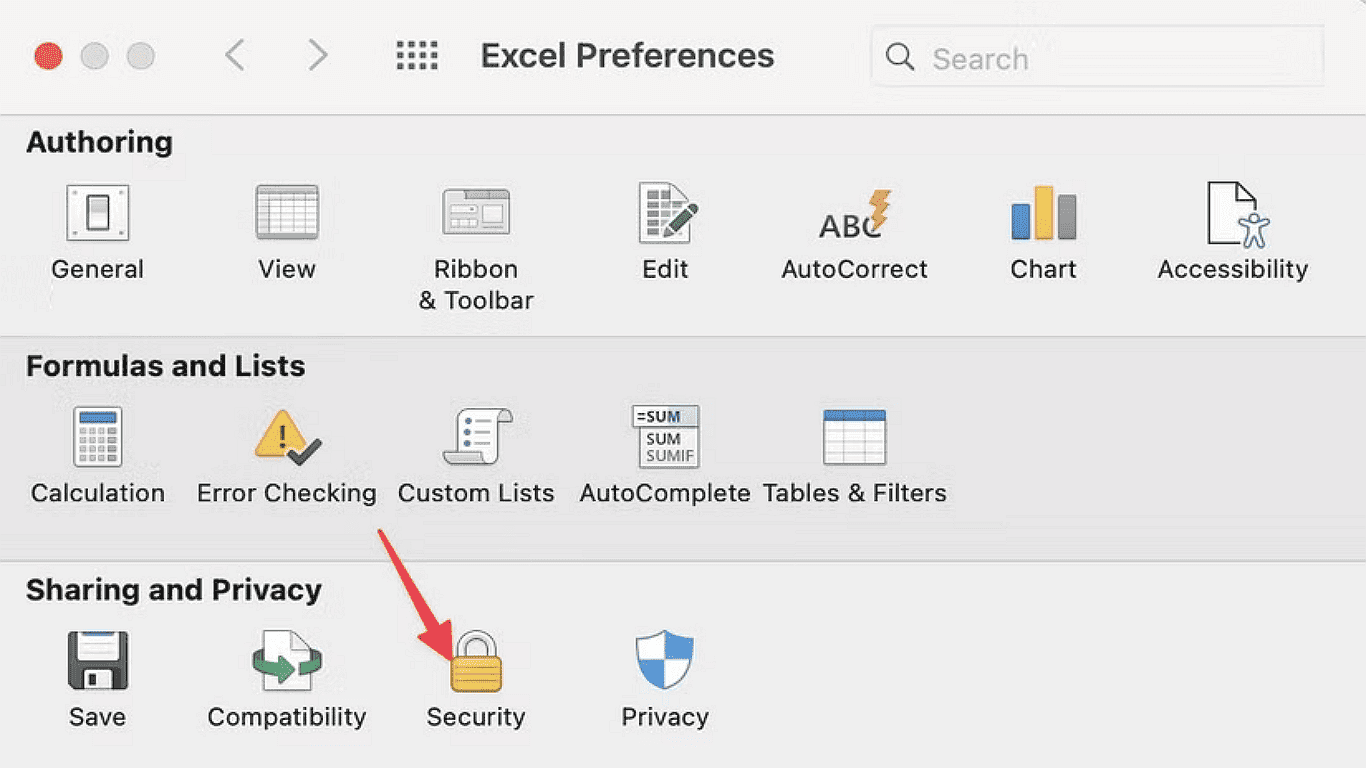
5.Click Macro Security to view available options

6.Select your preferred security level by clicking the corresponding radio button
Note: The available macro security options mirror those in Windows versions of Excel. For detailed explanations of each setting, please review the macro security options section mentioned earlier in this guide.
Best Practices for Using Macros Safely
Macros can boost productivity but pose security risks if misused. Follow these guidelines to minimize threats while benefiting from automation:
1. Verify File Sources
Do not enable macros in files from unknown senders especially unexpected email connections. Because cybercriminals often disguise malware as invoices, reports or other seemingly legitimate files. Avoid enabling content if you didn't request the File or the sender seems suspicious.
2. Use Digital Signatures
Indeed, digitally signed macros provide authenticity and confirm the identity of creator. Set macros to Disable all except digitally signed macros in Excel's Trust Center and only trust certificates from verified publishers to prevent running unauthorized code.
3. Maintain Strong Security Measures
Update your antivirus software regularly to detect macro based malware. Use strong passwords when sharing macro enabled files to prevent unauthorized edits that could introduce codes that are harmful.
4. Regular Backups Protect Data
Since macros can alter or corrupt files, maintain frequent backups of critical documents. Store copies in a secure location separate from your primary files. Always stay alert—even trusted files should be scanned before enabling macros.
Conclusion
Since macros can significantly enhance your Excel productivity but must be used cautiously to avoid security hazards. You can safely leverage their power while minimizing threats by following best practices such as verifying file sources, using digital signatures and adjusting security settings. You may find helpful resources at PDF Agile's Excel Tips for more Excel tips and advanced techniques.