In the high-stakes environment of the operating room, meticulous documentation is not just best practice—it's essential for patient safety and continuity of care. The operative note, or operative report, serves as the cornerstone of this documentation, providing a detailed account of the surgical procedure performed. This article will delve into the intricacies of operative notes, exploring their purpose, different types, key components, and offer a practical example to illustrate their importance in modern healthcare.
What are Operative Notes?
Operative notes are comprehensive medical documents that provide a detailed narrative of a surgical procedure. They are created immediately following a surgery by the surgeon or a member of the surgical team and become a permanent part of the patient's medical record. The primary goal of an operative note is to accurately and comprehensively document the details of the surgery, including the indications, procedures performed, findings, and any complications encountered. This information is crucial for communication among healthcare providers, for ensuring appropriate post-operative care, and for legal and quality assurance purposes.
Different Types of Operative Notes
While the fundamental principles remain the same, the level of detail and specific sections included in an operative note can vary depending on the complexity and type of surgery. Some common types or variations include:
- Standard Operative Note: This is the most common type, providing a detailed account of the entire surgical procedure.
- Brief Operative Note: In certain situations, such as minor procedures or those performed in an outpatient setting, a more concise version of the operative note might be used. However, it still includes the essential details.
- Post-Operative Note: This note is sometimes created separately or included at the end of the operative note to specifically document the patient's condition immediately after surgery, their disposition (where they are being transferred), and any immediate post-operative orders.
- Addendum to Operative Note: If there's any missing information or a need for clarification after the initial operative note is completed, an addendum can be added to supplement the original document.
Operative Note Example
Imagine a patient named Thomas Baker underwent a laparoscopic appendectomy performed by Dr. Robert Miller. Here's how his operative note might look:
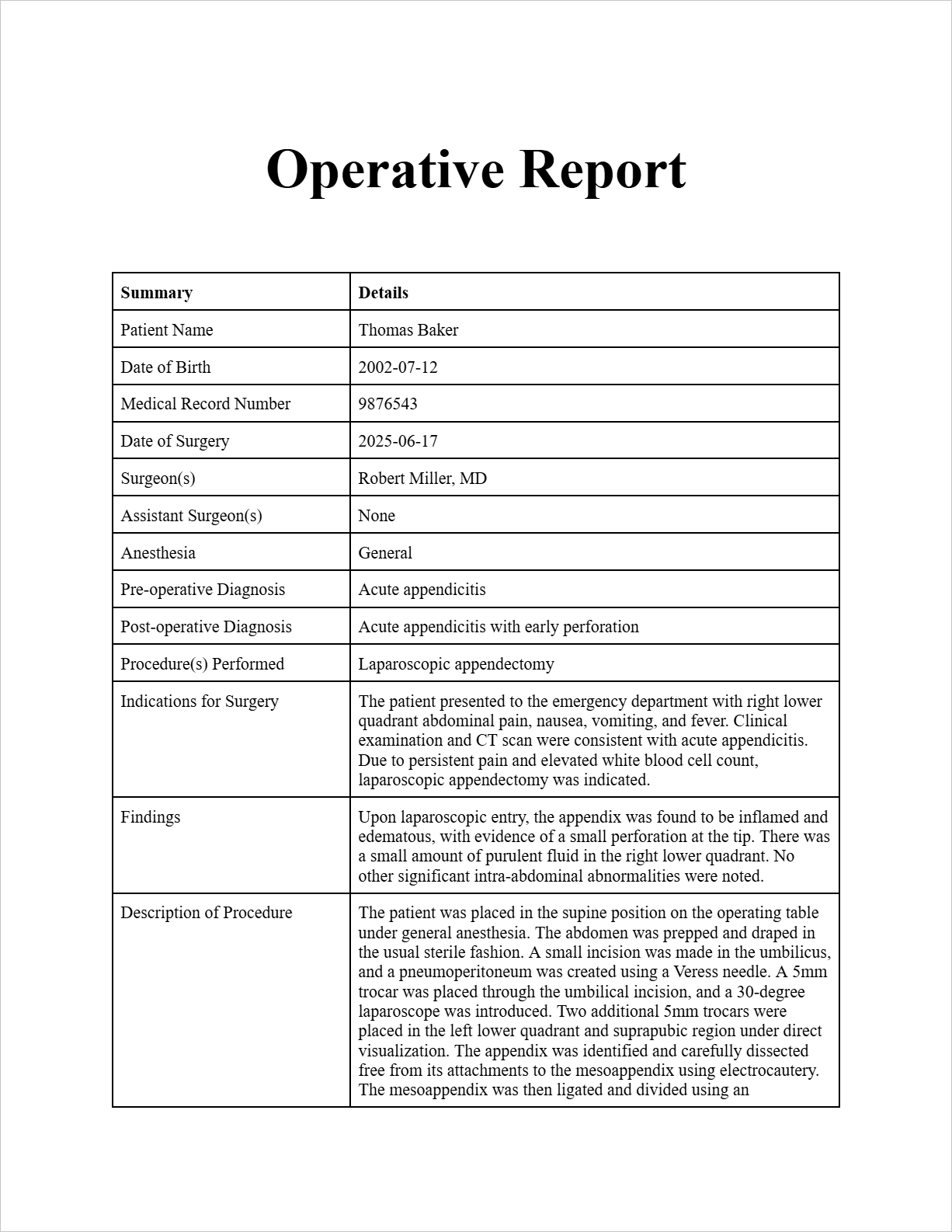
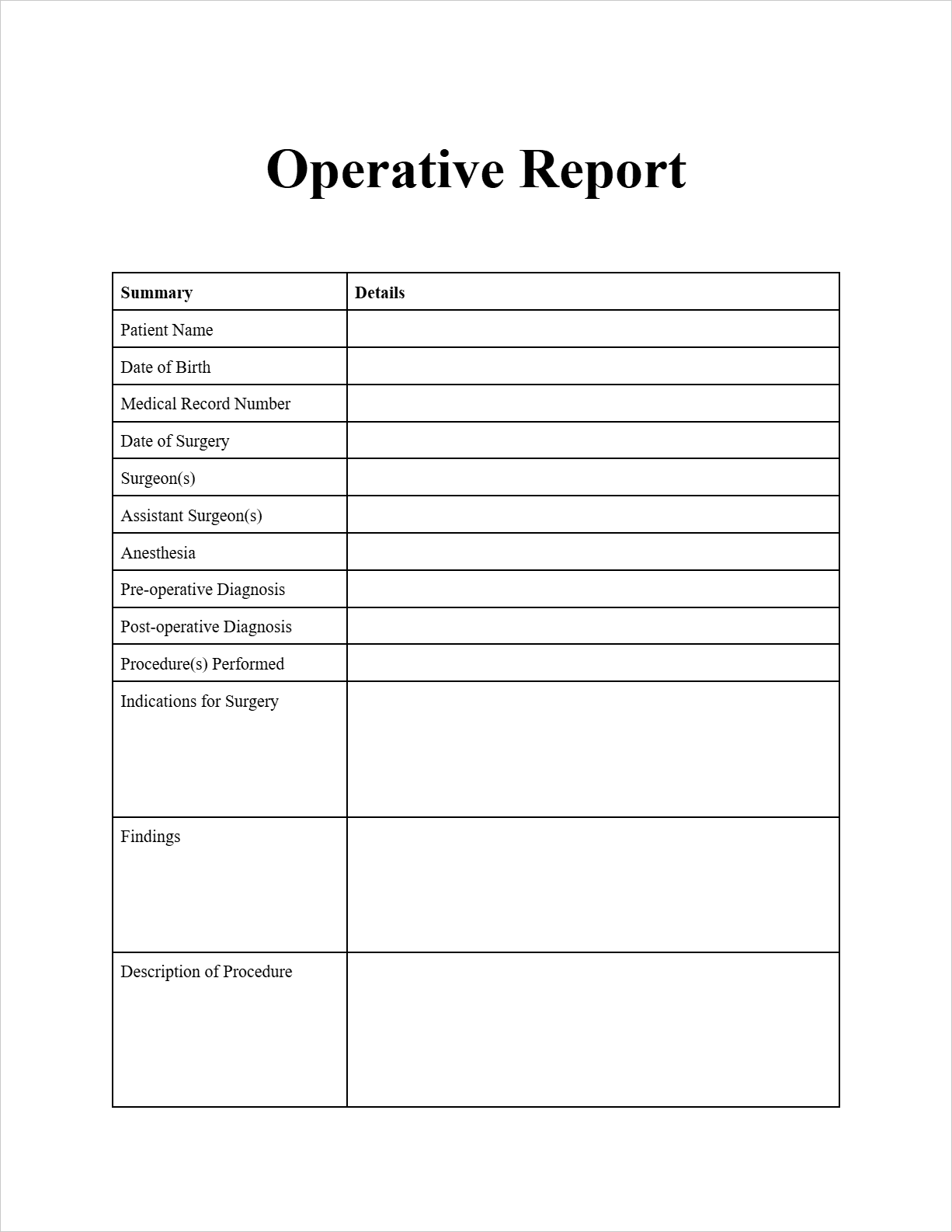
Operative Report
Patient Information:
Patient Name: Thomas Baker
Date of Birth: 2002-07-12
Medical Record Number: 9876543
Date of Surgery: 2025-06-17
Surgeon(s): Robert Miller, MD
Assistant Surgeon(s): None
Anesthesia: General
Pre-operative Diagnosis: Acute appendicitis
Post-operative Diagnosis: Acute appendicitis with early perforation
Procedure(s) Performed: Laparoscopic appendectomy
Indications for Surgery: The patient presented to the emergency department with right lower quadrant abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever. Clinical examination and CT scan were consistent with acute appendicitis. Due to persistent pain and elevated white blood cell count, laparoscopic appendectomy was indicated.
Findings: Upon laparoscopic entry, the appendix was found to be inflamed and edematous, with evidence of a small perforation at the tip. There was a small amount of purulent fluid in the right lower quadrant. No other significant intra-abdominal abnormalities were noted.
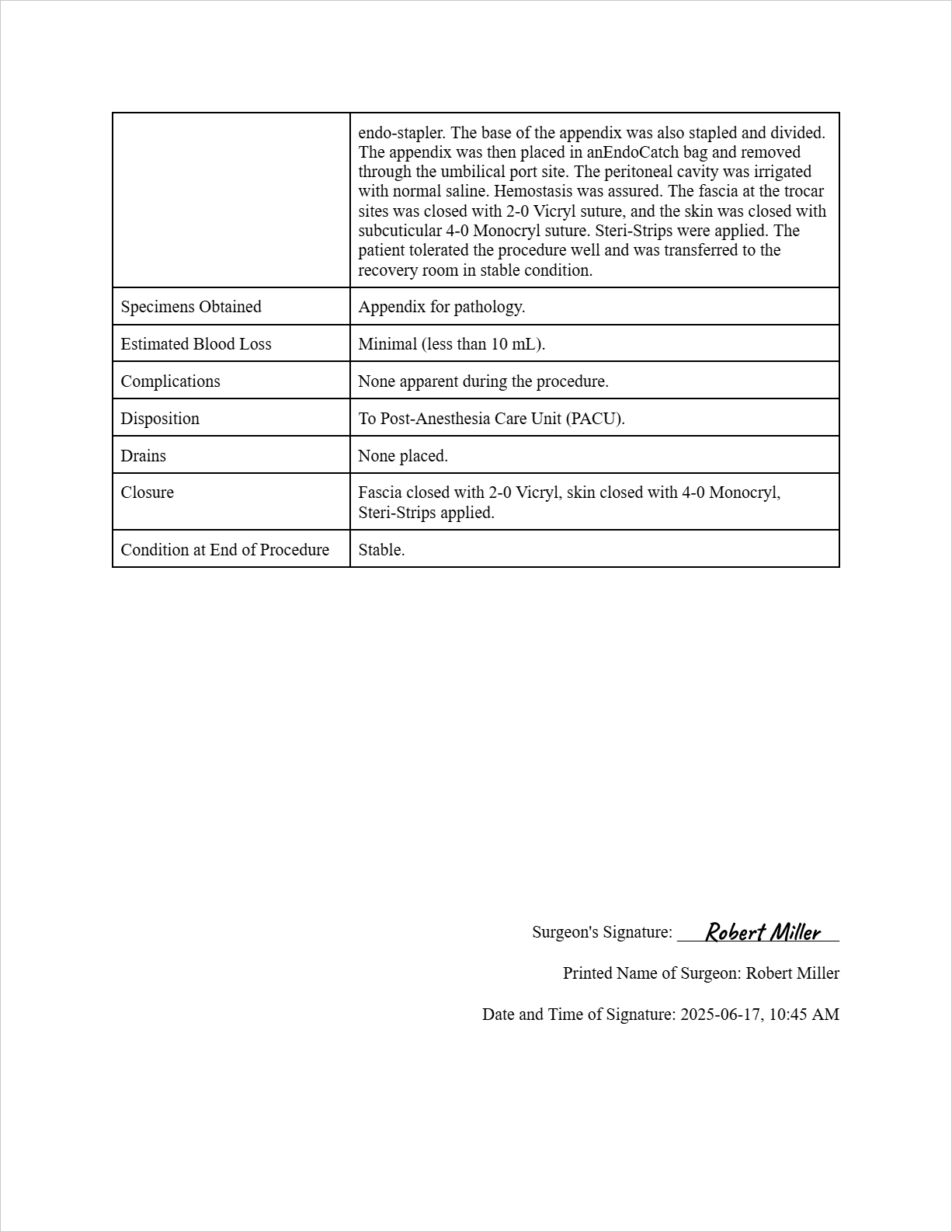
Description of Procedure: The patient was placed in the supine position on the operating table under general anesthesia. The abdomen was prepped and draped in the usual sterile fashion. A small incision was made in the umbilicus, and a pneumoperitoneum was created using a Veress needle. A 5mm trocar was placed through the umbilical incision, and a 30-degree laparoscope was introduced. Two additional 5mm trocars were placed in the left lower quadrant and suprapubic region under direct visualization. The appendix was identified and carefully dissected free from its attachments to the mesoappendix using electrocautery. The mesoappendix was then ligated and divided using an endo-stapler. The base of the appendix was also stapled and divided. The appendix was then placed in anEndoCatch bag and removed through the umbilical port site. The peritoneal cavity was irrigated with normal saline. Hemostasis was assured. The fascia at the trocar sites was closed with 2-0 Vicryl suture, and the skin was closed with subcuticular 4-0 Monocryl suture. Steri-Strips were applied. The patient tolerated the procedure well and was transferred to the recovery room in stable condition.
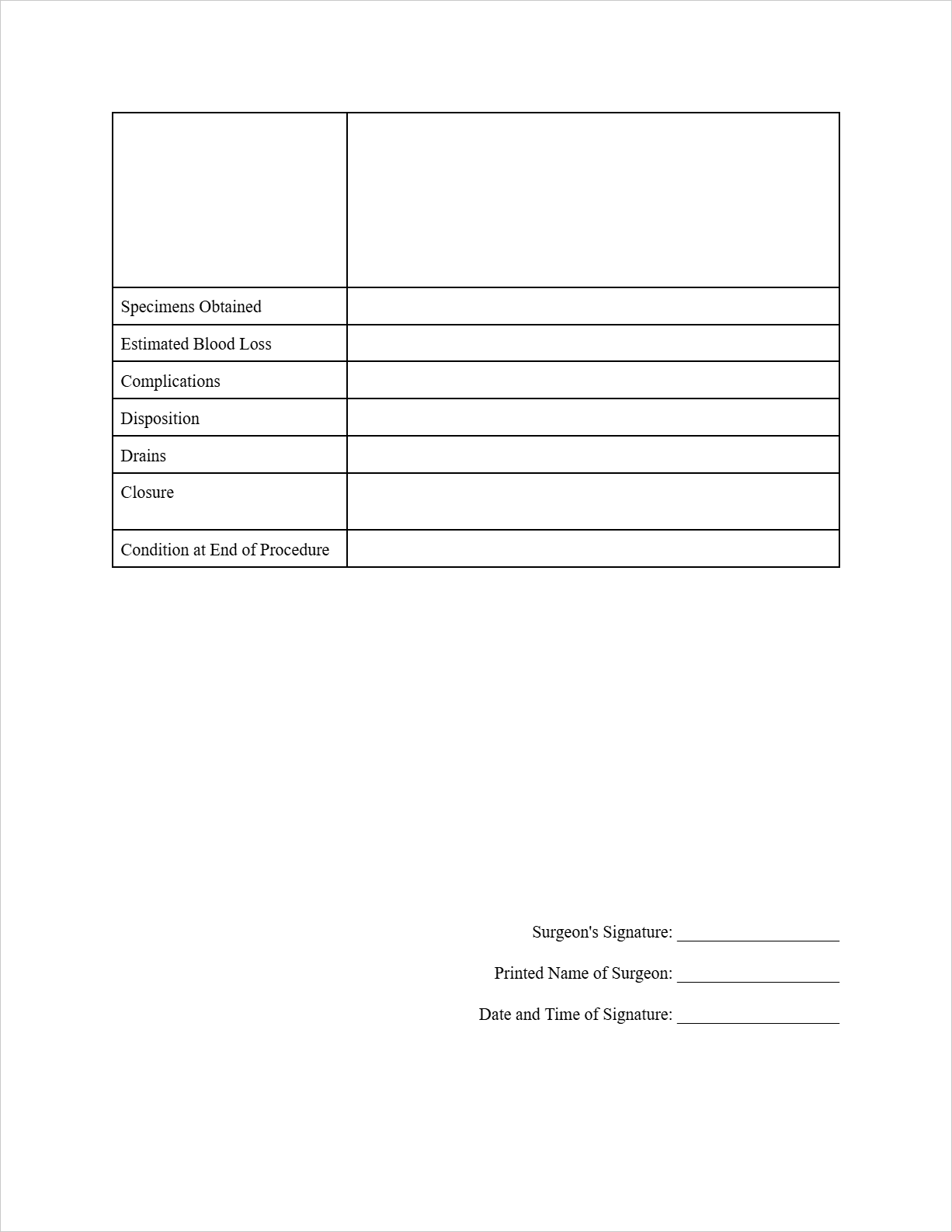
Specimens Obtained: Appendix for pathology.
Estimated Blood Loss: Minimal (less than 10 mL).
Complications: None apparent during the procedure.
Disposition: To Post-Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU).
Drains: None placed.
Closure: Fascia closed with 2-0 Vicryl, skin closed with 4-0 Monocryl, Steri-Strips applied.
Condition at End of Procedure: Stable.
Surgeon's Signature: (Imagine a signature is drawn here)
Printed Name of Surgeon: Robert Miller
Date and Time of Signature: 2025-06-17, 10:45 AM
FAQs about the Operative Note Template
Who is responsible for writing the operative note?
The primary surgeon is ultimately responsible for ensuring the operative note is completed accurately and in a timely manner. Often, a surgical resident or physician assistant may write the initial draft under the surgeon's supervision.
How soon after surgery should the operative note be completed?
Ideally, the operative note should be completed immediately after the surgery or within 24 hours to ensure accuracy and recall of all relevant details.
What level of detail is required in an operative note?
The operative note should be detailed enough to provide a clear and comprehensive account of the procedure. This includes all key steps, instruments used, findings, and any unexpected events or complications.
Why is the operative note so important?
Operative notes serve multiple critical purposes, including facilitating communication among the surgical team and other healthcare providers, providing a detailed record for post-operative care planning, serving as a legal document, and supporting quality improvement initiatives and research.
Where are operative notes stored?
Operative notes are a permanent part of the patient's medical record, whether it's in a paper-based system or an electronic health record (EHR).
Free Download: Printable Operative Note Template
You can download the Operative Note Template mentioned above by clicking Use Template button on this page. Customize it to fit your specific needs and preferences.