Cybercrime is an ever-evolving threat as technology advances, and 2025 is poised to see new developments in tactics used by cybercriminals. Below are the 7 most common digital threats to watch out for in 2025. We will also give you hints on how to protect yourself from cybercrime. Data leakage through embedded content is possible since PDFs carry hidden data in them in the form of embedded files, scripts, or metadata, which can leak sensitive information. The PDFs will have to be sanitized using tools by removing irrelevant metadata before being sent out. Attackers in Man-in-the-Middle can keep intercepted PDFs even over unsecured networks and tend to access sensitive data. To overcome this, data scientists should always send or share PDFs using encrypted email services or any other secure file-sharing services.
Good reasons to know the most common cybercrime threats for 2025
- Phishing and Spear Phishing Attacks: Attackers are increasingly sophisticated, maintaining the tempo of cybercrime trends. They also use convincing tactics, including AI-generated phishing emails. Business Email Compromise (BEC) schemes continue to grow, targeting executives or finance departments. Attackers also exploit fear and urgency, such as fake notifications related to security breaches, to lure victims.
- Ransomware Attacks: Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) has become a booming underground business, making it easier for non-technical criminals to launch attacks. Critical infrastructure, healthcare, and financial sectors are high-value targets, often facing devastating consequences if their systems are locked down. Double extortion tactics, where encryption and data theft occur, are becoming more prevalent.
- Deepfake and AI-Assisted Scams: Deepfakes are becoming harder to distinguish from real media, allowing attackers to impersonate individuals in sensitive positions (e.g., executives or political figures) with alarming accuracy. AI-powered scams are becoming more effective in evading detection and convincing victims of their legitimacy.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Attacks: Many IoT devices are vulnerable due to inadequate security features, making them prime targets for attackers. Often linked to critical systems, these devices can be compromised and serve as entry points into larger networks. Botnets using compromised IoT devices can be leveraged for Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
Comparison chart for the 7 most common cyber threats at a glance
Most common threats | Key features | Impacts | Preventive measures |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
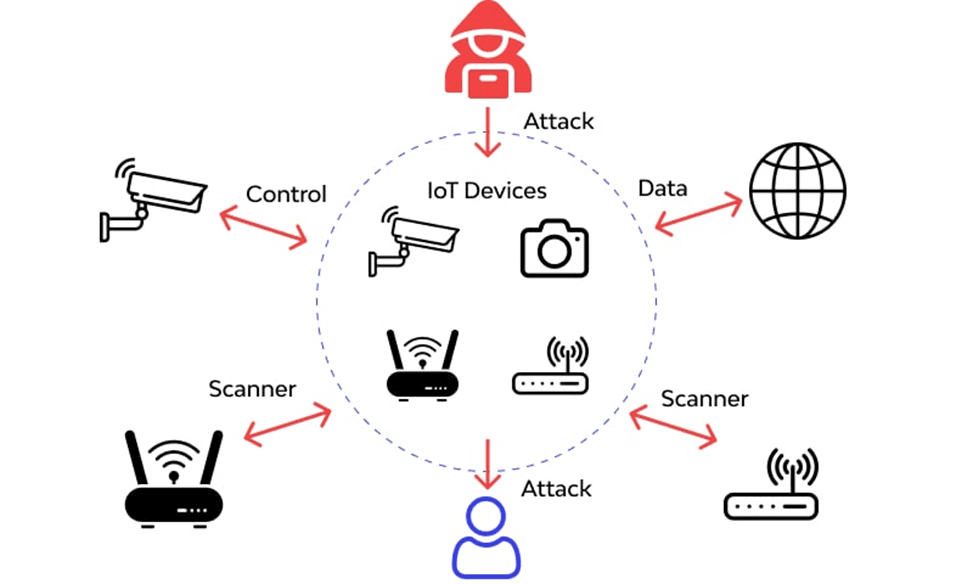
7 Most Common Cybercrime Threats
1. Phishing
- Description: This is the method by which emails or messages are sent, apparently originating from valid entities, to deceive people and reconcile them with personal information like passwords, credit card numbers, and login information.
- How it works: Attackers create fake websites or email links similar to any legitimate organization banks to social networking sites. In this, users get tricked into divulging critical information.
- Impact: It runs from identity theft, and financial fraud, to account compromise and breaches.
2. Ransomware
- Description: It is just a malware form that locks the information/data of a target in a way that would not be accessible until ransom from an attacker is paid.
- How it works: Ransomware spreads through phishing emails, malicious downloads, and security vulnerabilities. Further, it starts to lock files, and the entire system, and may raise demands for money afterward for compensation.
- Consequences: It causes critical loss of data, financial loss, loss of reputation, and disruption of work in businesses.
3. Malware
- Description: Software that is intentionally designed to be damaging to computers, networks, and devices maliciously.
- How It Works: There are several forms malware can take, which include viruses, worms, Trojans, spyware, and adware. Sometimes, malware spreads through phishing emails, infected websites, or through installed infected software.
- Impact: System damage, data theft, unauthorized access, and performance problems.
4. Denial-of-Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks
- Description: Denial of Service is a class of attack whereby an attack aims at the unavailability of the system, network, or server by overwhelming it with traffic.
- How it works: In DDoS, traffic originates from many compromised devices, and it is hard to mitigate such traffic.
- Impact: A website or services are down leading to financial loss, brand reputation, and potential loss of customer trust in an organization.
5. Man-in-the-Middle Attack
- Description: There is an invisible interloper between the two communicating parties in a MitM, while both believe they are communicating directly with each other.
- How it works: Attackers use unsecured or poorly encrypted Wi-Fi networks and conduct their attacks by exploiting vulnerabilities in several communication protocols.
- Impact: Data theft, espionage, compromised login credentials, and financial theft.
6. SQL Injection
- Description: SQL injection is an attack upon Web applications whereby the attacker embeds harmful SQL code into the query so he/she may have his/her way with the database.
- How it works: This can be done through the successful exploitation of input field vulnerabilities, which often search boxes on websites for gaining unauthorized access to the backend database to steal sensitive information.
- Impact: These might further lead to other possible digital threats such as data breaches, unauthorized access to sensitive information, manipulation of stored data, and even the compromise of an entire system.
7. Social Engineering
- Description: Social engineering is a form of attack whereby the hackers depend upon human manipulation rather than technical hacking. In this type, the attackers fool victims into supplying them with either personal or confidential information.
- How it works: The common ones are pretexting, baiting, tailgating, impersonation. Other than these, hackers take undue advantage of human psychologies, like those of trust, fear, or urgency to get what they want.
- Impact: Data theft, identity fraud, unauthorized access, and financial loss.
FAQs
Q: What is Denial of Service?
A: It would be regarded as DoS in such an attack when an attacker swamps the system or network with traffic in such a manner that overflows the system; hence the system cannot service or becomes unavailable to legitimate users.
The tips below can help you prevent it:
- Firewalls and Load balancer
- One can implement the software to monitor each traffic
Q: What is cyber espionage?
A: It is generally defined as stealing sensitive or confidential information on a computer. The targets are usually either governments or corporations.
How it works: Intrusions into systems for proprietary information are made by infiltrating into systems. Prevention: Deep cybersecurity policies and intrusion detection systems must be able to monitor the systems periodically.
Mention the general prevention tips against all cyber threats
- Anti-virus software shall be updated
- Periodically backup important data
- Use strong passwords for all accounts
- Enable two-factor authentication
- Never click on suspicious unsolicited emails, messages, and attachments
Q: How would I stay updated on any emerging cyber threat?
- Go through the cybercrime news and new updates published by authentic sources
- Attend webinars or conferences on cybersecurity
- Sign up for tips from legitimate cybersecurity organizations like the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency