Porter's five forces is a framework for assessing and evaluating a business organization's competitive strength and position. Porter's five forces airline industry is an analytical tool that uses five industry forces to explain why different industries can sustain different levels of profitability.
The five forces model of analysis is used widely across businesses, and most managers and strategists have heard of and probably used the framework. The framework can be applied (and re-applied) differently depending on the questions a business leader needs to answer.
Airline Industry porter's five forces analysis shows most airline industry companies face intense rivalry. The bargaining power of buyers in the airline industry is also relatively high. Unsatisfied customers might readily transfer airlines.
This industry is susceptible to changes in fuel prices. So even small changes can significantly impact profits, which results in low-profit margins. There are many new entrants in this industry, and the aircraft pricing is very volatile. This puts pressure on airlines to offer cheap, high-quality service.
This article will look at how the airline industry porter's five forces and analysis of industry competitors can help the sector.
Background of Airline Industry
| Name | Airline Industry |
| Type | Public Company |
| Industry | Airline |
| Total Companies | 5000+ |
Some experts argue that the airline industry has been around for over 100 years. It was discovered when Orville and Wilbur Wright made their first successful flight in Kitty Hawk, North Carolina, in 1903. Later, the Wright brothers formed The Wright Company and sold planes, engines, and spare parts but never flew commercially.
Air travel is a valuable and efficient way to travel, and it has grown by leaps and bounds over the last few decades. Here's Porter's five forces airline industry analysis that holds the future of air travel.

Airline Industry Porter's Five Forces
Porter's five forces airline industry model helps strategic business managers to analyze the industry in which their companies operate. This model, created by Michael Porter, determines the intensity of competition in an industry and its profitability.
Given the nature of the airline industry, it is no surprise that the level of competition is high. Legacy carriers, low-cost carriers, and regional airlines are all vying for market share. The entry barriers are also relatively high, given the need for extensive infrastructure and regulatory approvals.
Airline Industry Porter's five forces analysis model determines the strength of each of the following: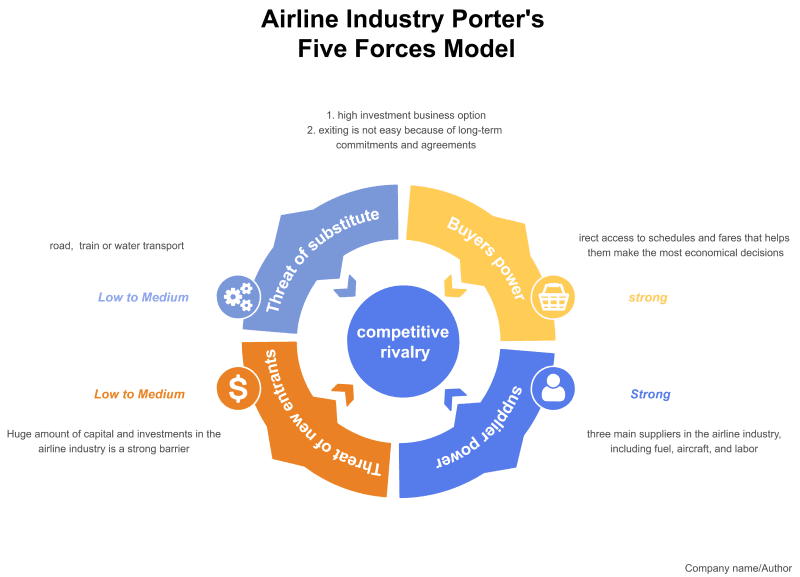
Competition In The Industry ( Strong Force)
Airline industry competitor analysis reveals that the competition in the industry is intense. In the early days of aviation, only a few major players were in the game. One airline would usually dominate the market, with little to no real challengers.
Today, many different airline companies are competing for market share. Each airline can only fly to so many destinations, meaning that they all compete for the same routes and customers.
Apart from this, the airline industry has to attract customers by pampering the fliers. That's why low-cost carriers don't get a chance, and larger companies have to count on more expenditure.
The Threat Of New Entrants ( Low to Medium Force)
According to Porter's five forces airline industry model, the threat of new entrants possesses low to medium force. The low threat of new entrants in the airline industry is because it is capital intensive.
To run a successful airline business, owners will have to invest huge money in acquiring aircraft, building a terminal, acquiring land for the airport, hiring skilled pilots and cabin crew, and ground personnel. Once these elements are in place, the owner will have to spend a considerable amount on technological advancement.
Besides this, a newcomer has an option to connect with some other established companies or use their resources. These resources are the ones that work towards cutting down the cost of operation of your business.
The Bargaining Power Of Suppliers (Strong Force)
The bargaining power of suppliers in the airline industry poses a strong force as fuel, aircraft, and labor are all affected by the external environment. The airline industry is highly volatile because of its dependence on oil prices. As a result, there is a high risk for airline companies to increase ticket prices.
On the other hand, Aircraft are enormous and expensive machines subject to constant innovation and improvement. As famous as Boeing is, It could change an aircraft model, and most airlines would purchase it without questioning its technological advancement to hit the jackpot.
The Bargaining Power Of Consumer ( Strong Force)
Porter's Five Forces Airline Industry model focuses on the consumer as consumers are the ultimate buyers! They are the final decision maker when it comes to choosing any product. Consumers have significant power because they vote with their money, and if a company has a product of inferior quality, the company will lose its customers very fast. Consumers can also take their business elsewhere in search of other alternatives.
Consumers are also susceptible to price changes. Even a slight price increase can cause a significant fall in sales.
Threat Of Substitute Products and services
There are multiple substitutes for air travel. The most obvious is the automobile. The amount of time and energy that people spend on automobiles is extraordinary. So we can say that it exerts medium force.
The threat of substitutes is an important factor when analyzing industries. For example, if a buyer perceives that he has alternatives in purchasing an airline ticket, he would most likely not buy the ticket.
The substitute products or services are usually similar to the original item. Moreover, companies offer substitute products or services within the same industry.
Strategies For Success
Cost leadership
A cost leadership strategy is used when a company focuses on meeting the lowest possible cost. Cost leaders are generally not concerned with innovating or creating new products as they try to become more efficient than their competitors. There is no such thing as a fully-fledged cost leader in this industry, but there are airlines that focus on being low-cost operators.
Differentiation
The airline industry adopts a differentiation strategy to offer high-quality services at premium rates. It is the best bet to thrive in the competitive market as cost leadership alone isn't enough to generate a handsome profit.
Focus
Focus strategy enables businesses to launch creative services and products for the consumers. These services usually identify small-scale segments and introduce special services for each age group. A unique geographical route is the best tactic to grab customers' attention in the airline industry.
Key Takeaways
Porter's Five Forces airline industry model is a valuable tool for examining industry competitiveness. In this article, we took a closer look at how each of Porter's five forces impacts the airline industry.
These five forces are derived from industrial organization economics and help define how competitive a market is and how profitable it is (or isn't). Cost leadership, differentiation, and focus are the success strategies to hit the jackpot.
PDF Agile is a desktop app that is changing the way in which businesses operate. PDF Agile allows you to handle documents without changing the format, whether you want to edit, convert, or compress the document.
References
Greg Depersio "Analyzing Porter's 5 Forces Model on Delta Air Lines" Available at: https://www.investopedia.com/articles/markets/012816/analyzing-porters-five-forces-delta-airlines-dal.asp
Prachi Juneja "Porter's Five Forces Analysis of the Airlines Industry in the United States" Available at: https://www.managementstudyguide.com/porters-five-forces-analysis-of-airlines-industry-in-united-states.htm
"Airline Industry Porter's Five Forces Analysis" Available at: https://www.edrawmax.com/article/airline-industry-porters-five-forces-analysis.html